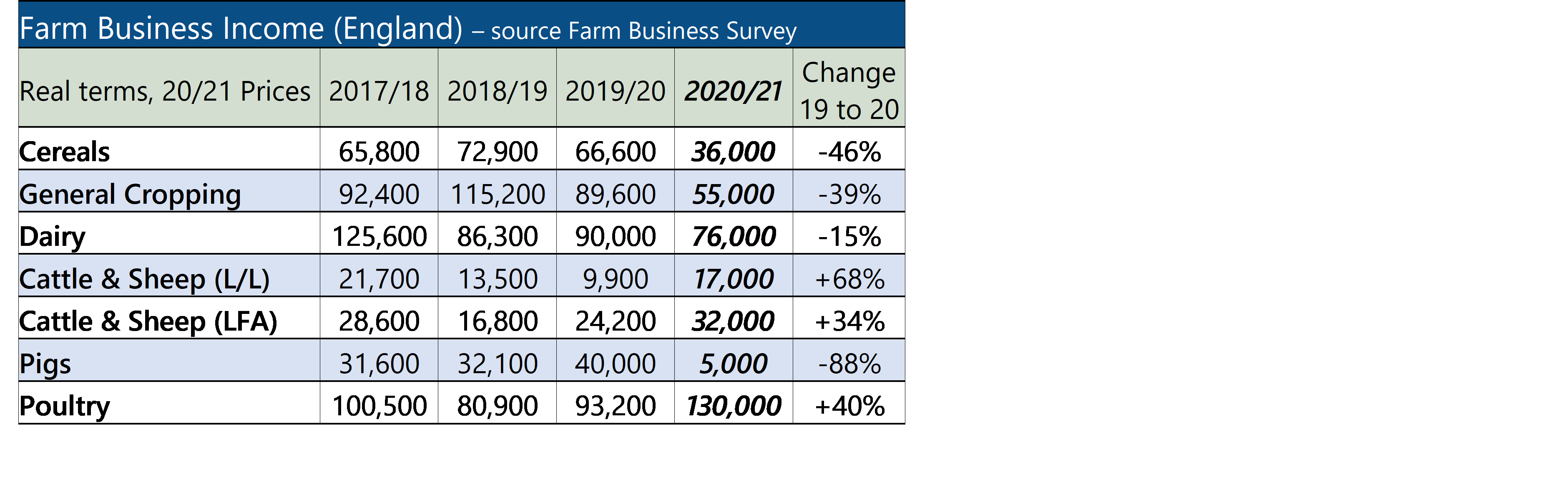
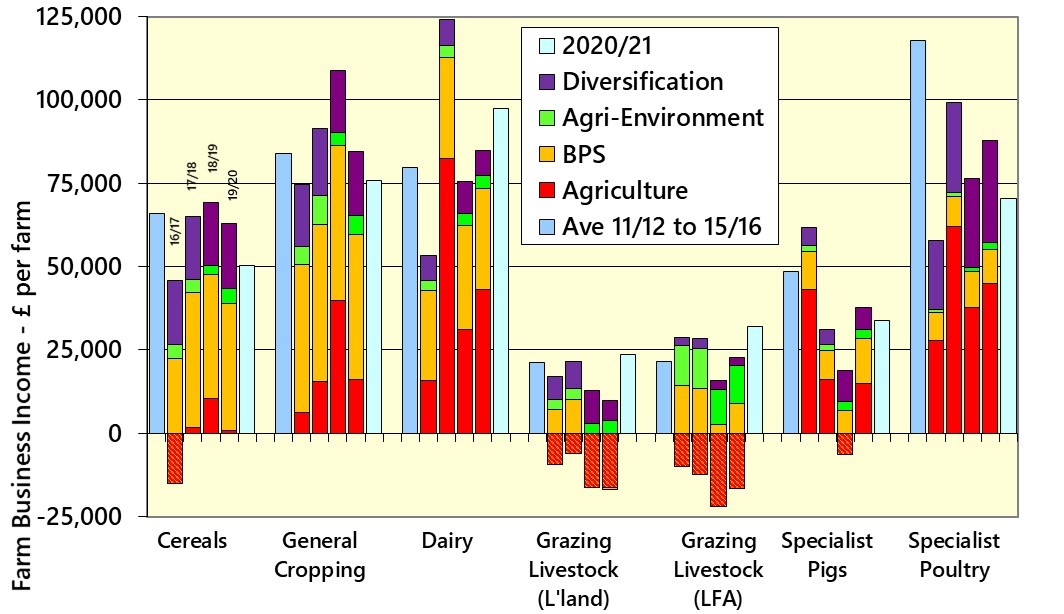
The long-awaited Defra consultation on Lump Sum payments and Delinking of the BPS has finally been published. The consultation seeks views on who should be eligible for the Lump Sum payments and how these and Delinked payments should be calculated.
Lump Sum Payments
These will be offered to those who wish to exit the industry. Defra’s intention is that there will be a one-off application window in 2022 with no scope to apply after that. Proposed conditions and eligibility rules include:
- Only those who claim the BPS will be eligible, it is an exit scheme and therefore there will be no age restrictions. To prevent recent entrants from leaving with a lump sum, Defra is proposing that applicants must have made their first Direct Payment (BPS) claim in 2015 or earlier.
- The BPS applicant would have to give up their land in England.
- An owner/occupier would have to sell and/or rent out their land, or transfer by gift. The proposal is if an owner/occupier decides to rent out their land this must be via an FBT and for a minimum of five years.
- A Tenant must surrender their tenancy, this can be a Farm Business Tenancy (FBT) or An Agricultural Holdings Act (AHA) tenancy. AHA tenants will also be eligible if they pass on their tenancy under a succession.
- Those receiving a Lump Sum would be able to retain occupation of their residential and commercial property and up to 5% or 5ha (whichever is the smaller) of their land.
- All English BPS entitlements held by the applicant would be cancelled, including any that have been leased-in from another farmer. Those that have been leased-out would be cancelled at the end of the lease. This could present a problem where a Landlord has leased or Transferred entitlements to a Tenant with an obligation to return to the Landlord – will the Landlord accept the Surrender if he will be left with land without any entitlements?
- It will be an all-or-nothing scheme – it will not be possible for applicants to keep some entitlements and take a partial Lump Sum payment.
- If a Lump Sum payment is received, the farm business cannot claim any further direct payments (BPS). This includes any Directors of a Limited Company and all Partners of a Partnership. If any recipient enters into a new land management agreements (or adds land to an existing agreement) such as Countryside Stewardship or ELM, during the Agricultural Transition, the Lump Sum payment will have to be repaid.
- The tax treatment of Lump Sum (and Delinked) payments is currently being discussed with HMRC and guidance is expected shortly. This will be crucial to how attractive the ‘offer’ is to many farmers – i.e. will the payment be taxed as capital or income.
With regard to the actual payments, Defra expects to be able to fund all the eligible applications it receives and therefore it will not be a competitive scheme. There will be no rules on what the lump sum can be spent on. The amount a claimant will receive will be;
Lump sum Reference Amount X 2.35
A 2.35 multiplier means the payment will be approximately equivalent to the amount a farmer could have received in Direct Payments for 2022 to 2027 under the phasing out of the BPS. The Reference Amount will be the average value (if more than one year is used) of BPS received (for English entitlements) before any penalties or progressive reductions have been applied in a Reference Period. Defra is asking for views on the Reference Period, but is proposing a three-year average based on 2018, 2019 and 2020 BPS years.
There is a proposed payment cap of £100,000, meaning a maximum Reference Amount (average BPS claim) of about £42,500 would not be affected by the cap. There will be measures put in place to deal with changes to farm businesses since the start of the reference period (‘mergers and scissions’) and also to prevent artificial changes to businesses to claim payment.
Full rules for the Lump Sum scheme are promised by the end of October this year. This is to allow time for farmers to consider the merits of the scheme (and potentially Tenants to negotiate with Landlords) before applications are invited in ‘early 2022’.
Defra has clearly said exiting farmers will have to give up their entitlements. It has also stated that it intends to end the New and Young Farmers National Reserve scheme (offering free entitlements) from 2022, meaning from next year we could already see land which will not have any entitlements over it. On the face of it, it looks like new entrants will be losing out, which seems strange as part of the reason for the Lump Sum encourage new and young entrants by freeing-up land. Defra has said the proposal will create ‘more lasting opportunities for new entrants to access land’ and in the press release it has said it is working on a scheme with industry leaders, local councils, land owners and new entrants on a New Entrants Scheme. This will be available in 2022 with details expected to be published later this year.
Delinked Payments
These are expected to be introduced in 2024 and will mean businesses can reduce the area they farm or even cease farming and they will still receive payments for the rest of the Transition Period. Delinking will not be optional. Delinked payments will be made to those who were receiving a BPS payment in a Reference Period (see below) and in 2023 (if the Reference Period is earlier than this). Defra has said Tenants who received BPS during the Reference Period, and still farm at the end of it should be eligible to receive the delinked payment. Again, this throws up questions about Tenancies which end during the Agricultural Transition; it seems to suggest that the Tenant will receive the Delinked payment and the Landlord will not have a payment to ‘give’ to a new Tenant.
The actual payments will be calculated for each year from 2024 to 2027 based on the BPS payments made to the applicant in the Reference Period less the progressive reductions for each year. Defra is asking for views on the Reference Period. It is proposing the average of 2018 to 2020 (the same as the Lump Sum) for ease, but acknowledges a longer period, which includes 2021 and 2022 would take account of more business changes.
Defra acknowledges that Delinking payments means there will no longer be an annual BPS claim, meaning it loses data on land use. Having no link between payments and land also means cross-compliance will no longer operate. These points are not part of this consultation, indicating there will be another consultation later.
The consultation is open from 19th May until 11th August. The full consultation document can be found at https://consult.defra.gov.uk/agricultural-policy/lump-sum-and-delinked-payments-england/supporting_documents/lumpsumexitschemedelinkedpaymentsconsultation.pdf. Responses can be made online via https://consult.defra.gov.uk/agricultural-policy/lump-sum-and-delinked-payments-england/
Whilst the detailed scheme rules for the Lump Sum will not be known until October, those potentially wanting to take advantage of it should be having discussions with the relevant parties (bankers, advisors, landlords, etc.) sooner rather than later.